Fluorine in the wastewater from a semiconductor plant is treated with an adsorbent after coagulating sedimentation treatment

Contents
1.Implementation site of “READ-F(HG)” adsorbent for water treatment used to treat fluorine?
4.Flow of fluorine treatment using “READ-F(HG)” adsorbent for water treatment
5.Fluorine removal using “READ-CX” flocculant for water treatment
6.Running costs for fluorine treatment using “READ-CX” flocculant for water treatment
Implementation site of “READ-F(HG)” adsorbent for water treatment used to treat fluorine?
Semiconductor plant
Treating fluorine in water
It is believed that fluorine is an effective means of preventing cavities when used in small quantities. Excessive ingestion of fluorine is shown to induce symptoms such as tooth hypocalcification and osteosclerosis and it could possibly be fatal.Coagulating sedimentation is a common way of treating fluorine, but its effectiveness is low when treating wastewater to a low concentration. For this reason, another advanced method for treating wastewater is necessary. Fluorine-containing wastewater may be treated by means of coagulating sedimentation using calcium, coprecipitation of hydroxide, adsorption (“READ-F(HG)”) or a combination of these methods.
The following is an example of the use of an adsorbent to perform advanced treatment following the calcium-based coagulating sedimentation of fluorine in wastewater from a semiconductor plant.
Example of fluorine treatment using “READ-F(HG)” adsorbent for water treatment at a semiconductor plant
Since semiconductor plants must treat the hydrofluoric acid-derived fluorine contained in their wastewater, calcium-based coagulating sedimentation is followed by advanced treatment using an adsorbent.
As wastewater is continually generated, multiple towers are used to treat it. This enables the continuous treatment of wastewater, even during regeneration.
The adsorbent can also be used as a safety device, thus enabling a reduction of operational costs by prolonging the regeneration period.
Results of fluorine treatment using “READ-F(HG)” adsorbent for water treatment
Treatment concentration: F = 15 → 2 mg/L, quantity of treated water: 25m3/hr
Flow of fluorine treatment using “READ-F(HG)” adsorbent for water treatment
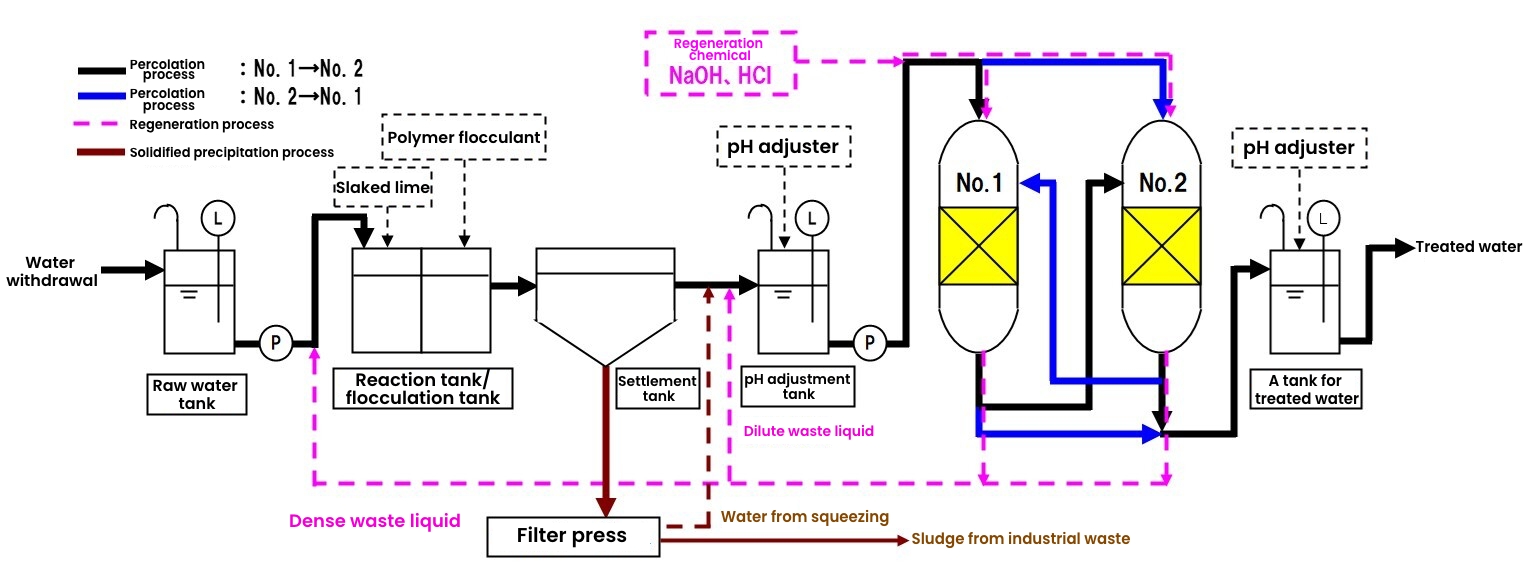
The flow shown in the above diagram assumes the use of an Air Water Group adsorbent.
The advantages of solidified precipitation and adsorption are combined to stabilize treatment and reduce running costs.
Since it requires an initial equipment investment, our proposals also encompass amortization costs and are aimed at improving the site.
About Fluorine removal using “READ-CX” flocculant for water treatment
As a flocculant, “READ-CX” works very well for the treatment of fluorine.
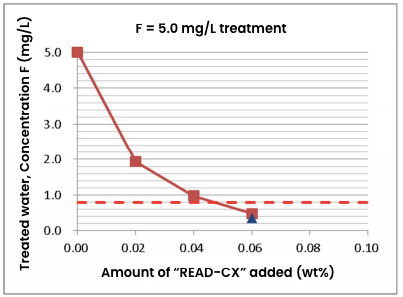
Unlike the calcium method, it can also be used for the treatment to within a low concentration range.
It also helps inhibit the generation of sludge as adding even a small amount of READ-CX can be highly effective.
There are no concentration restrictions for “READ-CX” and it can enable treatment to a low concentration depending on the volume added to the system.
The graph below shows the addition of “READ-CX” to the simulated liquid at 5 mg/L, lower than the wastewater standard, is able to treat the wastewater up to the environmental standard value of 0.8 mg/L.
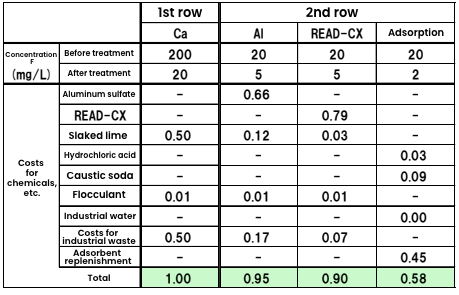
Running costs for fluorine treatment using a “READ-CX” flocculant for water treatment
In comparison with aluminum coprecipitation, “READ-CX” works at smaller quantities and can also help reduce costs.
Adsorption significantly reduces running costs but requires an initial investment.
“READ-F(HG)” adsorbents and “READ-CX” flocculants are recommended for the advanced treatment of fluorine-containing wastewater
“READ-F(HG)” was introduced in the semiconductor plant. This is “READ Series” adsorbent product for water treatment and is designed for treating fluorine-containing wastewater.
A characteristic of “READ-F(HG)” is that it is highly selective for fluorine, which makes it possible to remove fluorine even when it is mixed together with many foreign substances.
Washing the adsorbent with an acid or alkali can desorb the fluorine that has been adsorbed. This enables repeated use and leads to a reduction of running costs.
Unlike other flocculants, “READ-CX” can be expected to perform to a degree even within a low concentration range.
For this reason, treatment using “READ-CX” can be done using existing solidified precipitation devices, without requiring an equipment investment like an adsorption tower.
It works at smaller quantities than the aluminum chemicals designed for similar treatment. This also controls the amount of sludge generated.
“READ-CX” is mainly used at facilities such as coal-fired power stations, semiconductor plants, auto manufacturing plants and metal surface processing plants.


