READ series for water treatment
ー Selective adsorption and removing hazardous substances in the target water by using the adsorbents in accordance with different elements.
It can help to reduce the costs with its high performance of adsorption and convenient regeneration treatment.
Features of the READ series of
adsorbents for water treatment
Has a high selectivity for specific elements
Because of the high selectivity, the adsorbent can remove specific elements such as fluorine, arsenic and boron which are comparatively hard to treat even from the liquids like seawater that contains many impurities.

Possible to regenerate & recycle and has superior economic efficiency
It is superior in economy because the adsorbent can be use repeatedly by washing it with acid and alkali to desorb the adsorbed elements and regenerate it.
Porous shape enables the high performance of adsorbent
In READ series, pores can be created inside the adsorbents by special technology.Therefore, this enables the water to permeate both the surface and inside of adsorbent and to gain the high performance.
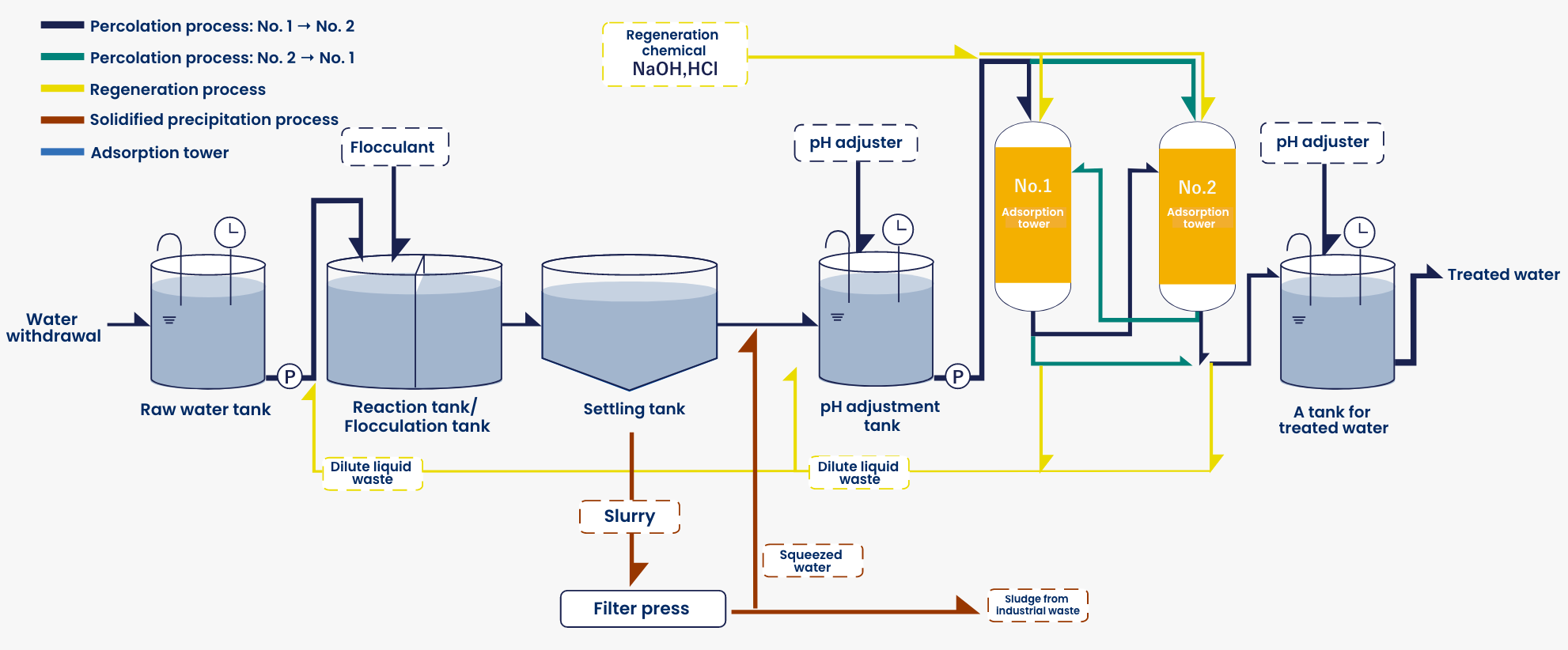
Principle of water treatment by using the READ series
The target elements in the liquid can adsorbed and removed when an adsorption tower is filled with resin to enable the liquid flow through.
List of water treatment adsorbent, “READ series”
Adsorbents for arsenic: READ-As
“READ-As” is highly adsorptive and can be used without pretreatment either in a trivalent or pentavalent form. Since an arsenic is highly toxic, the effluent standards are low and used at a low concentration, therefore, it has a feature that the regeneration cycle is very long in many cases. For this reason, we mostly regenerate an adsorbent at Air Water Group plants, not on site.
Adsorption &
Regeneration mechanism
Pentavalent arsenic:
Ce(OH)4 + AsO43- → Ce(AsO4)(OH) + 3OH-
Trivalent arsenic:
Ce(OH)4 + AsO33- → Ce(AsO4) + 3OH- + 3H+
Where are they used?
Treatment of springwater on construction and tunnel sites and purification of well water for food factories
Basic physical
properties of resins
| Product name | READ-As |
|---|---|
| Adsorption object | Cerium hydroxide |
| Appearance | Yellow oval and spherical shape |
| Average particle size | 0.6~0.8mm |
| Wet true specific gravity | 1.45~1.65 |
| Effective pH range | 5~10 |
| Regeneration treatment | Possible with alkali |
| Other | Passed the water supply materials and equipment elution test |
Adsorbents for fluorine: READ-F, READ-F (HG)
“READ-F” and “READ-F (HG)” are highly adsorptive and have been used for many years.Fluorine-containing wastewater comes from thermal power stations, semiconductor factories and other facilities and generally treat with coagulation sedimentation by using calcium. However, it is hard to lower the effluent standards by using a coagulation sedimentation treatment alone. Ideally, coagulating sedimentation should be combined with an adsorption method.
Adsorption &
Regeneration mechanism
Adsorption:Ce-OH + F- → Ce-F + OH-
Regeneration:Ce-F + NaOH → Ce-OH + Na+ + F-
Washing with alkali desorbs and resubstitutes the adsorbed fluorine with a hydroxyl group.
Where are they used?
Wastewater treatment at semiconductor factories and auto parts factories
Basic physical properties of resins
| Product name | READ-F | READ-F(HG) |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption object | Cerium hydroxide | Cerium hydroxide |
| Appearance | Yellow oval and spherical shape | Yellow oval and spherical shape |
| Average particle size | 0.6~0.8mm | 0.6~0.8mm |
| Wet true specific gravity | 1.4~1.6 | 1.9~2.1 |
| Effective pH range | 3~3.5 | 3~3.5 |
| Regeneration treatment | Possible with alkali | Possible with alkali |
| Features | Low-cost adsorbents for wastewater | It exhibits performance nearly twice as high as READ-F because the supported amount of cerium has increased. |
Adsorbents for boron: READ-B, READ-B (MC) and READ-B (LC)
“READ-B” is highly effective in the treatment of wastewater at a high concentration.Aside from “READ-B”, “READ-B (LC)” is a chelate adsorbent for boron and usable for beverages. “READ-B (MC)” works well even at low to medium concentrations. Effectively combining other treatment methods and adsorbents can increase treatment efficiency and reduce costs.
Adsorption &
Regeneration mechanism
Adsorption:Ce-OH + B(OH)4- → Ce-B(OH)4 + OH-
Regeneration:Ce-B(OH)4 + NaOH → Ce-OH + B(OH)4-+Na+
At a low concentration of boric acid, it exists in a H3BO3 state at pH7 or lower and in a B(OH)4- state at pH7 or higher. As the concentration rises, boric acid becomes a circular or chain-like polynuclear compound (a polymer) and form into B5O6(OH)4-, B4O5(OH)52-.
Where are they used?
Wastewater treatment at electronic parts factories, power stations and refuse disposal facilities and use for the desalination of well water and seawater
Basic physical properties of resins
| Product name | READ-B | READ-B(MC) | READ-B(LC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorption object | Cerium hydroxide | Macroporous type & Styrene type | Macroporous type & Styrene type |
| Appearance | Yellow oval and spherical shape | White opaque and spherical shape | White opaque and spherical shape |
| Average particle size | 0.6~0.8mm | 0.6~0.8mm | 0.6~0.8mm |
| Wet true specific gravity | 1.7~1.9 | 1.08~1.18 | 1.1 |
| Effective pH range | 7~9 | 5~10 | 5~10 |
| Regeneration treatment | Possible with acid and alkali | Possible with alkali | Possible with alkali |
| Other | Passed the water supply materials and equipment elution test | ー | Acquired WRAS approval in the United Kingdom and certified for use in beverages by the NSF in the United States. |
| Features | A concentration dependence is high and when it becomes high, the amount of adsorption increases. | Chelate is highly selectivity and is less vulnerable to the effects of inhibitory components. | Chelate is highly selectivity and is less vulnerable to the effects of inhibitory components. |
Adsorbents for heavy metals: READ-HM
Wastewater standards have been established that regard heavy metals as hazardous substances that can affect people's health and farm produce. “READ-HM” is used to remove heavy metals such as copper, lead and cadmium.
Where are they used?
Spinning mills and factories of processing metal surfaces
Basic physical properties of resins
| Product name | READ-HM |
|---|---|
| Adsorption object | Macroporous type & Styrene type |
| Appearance | Pale yellow opaque and spherical shape |
| Average particle size | 0.43~1.18mm |
| Wet true specific gravity | 1.1~1.2 |
| Effective pH range | 2~6(Type H)、6~11(Type Na) |
| Regeneration treatment | Possible with acid and alkali |
| Other | It can adsorb the general heavy metals and can treat many different elements. |
Adsorbents for phosphoric acid: READ-P
Phosphorus is known to be a substance causing eutrophication and the environmental standards have been set for it. It is highly selectivity and used in applications such as the removal of phosphorus from plating wastewater.
Where are they used?
Factories of processing metal surfaces
Basic physical properties of resins
| Product name | READ-P |
|---|---|
| Adsorption object | Cerium hydroxide |
| Appearance | Yellow oval and spherical shape |
| Average particle size | 0.6~0.8mm |
| Wet true specific gravity | 1.7~1.9 |
| Effective pH range | 3~10 |
| Regeneration treatment | Possible with high-concentration alkaline |
| Other | The adjustment of pH is hardly necessary for this product as it has a broad effective pH range. |
Where are the READ series of adsorbents for water treatment used?
Fluorine adsorbents are mostly used at semiconductor-related factories. The machine industry, power stations and in industry-based place are the second place to use for the wastewater treatment.
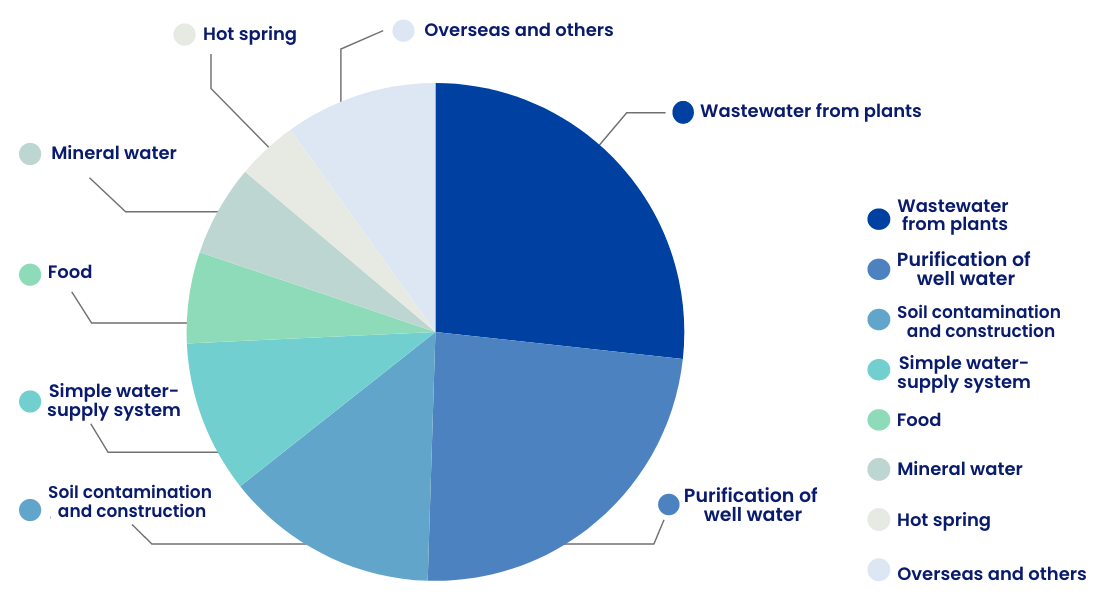
Arsenic adsorbents are used at many other applications involving either wastewater or purified water such as to treat wastewater from factories and to purify well water.
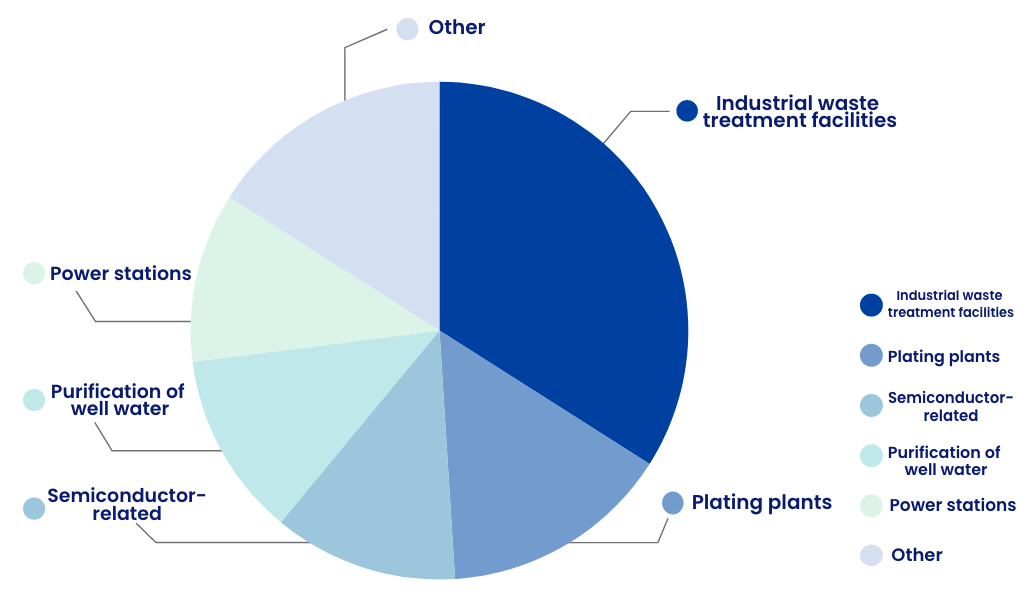
Boron adsorbents are mostly used at industrial waste treatment facilities and are also commonly used to treat industrial wastewater from plating plants, semiconductor plants and other facilities.
Delivery data of fluorine adsorbents
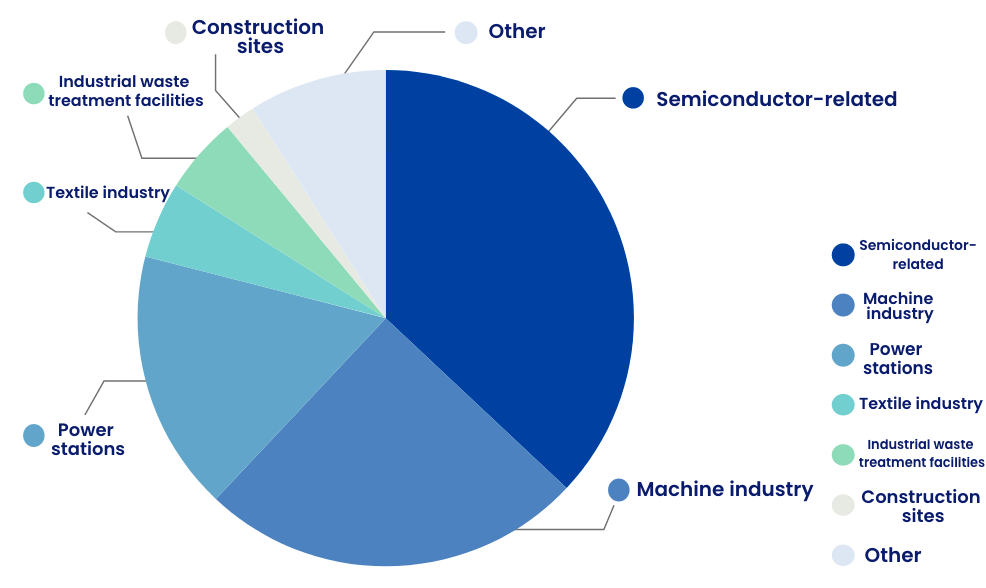
Delivery data of arsenic adsorbents
Delivery data boron adsorbents
Implementation examples
-

Boron in desulfurization wastewater from a thermal power station is removed using a flocculant | Additional information about adsorbents
An excessive amount of boron can adversely affect the growth …
-

Treatment of detected arsenic from a tunnel springwater by using an adsorbent
Arsenic is carcinogenic and affect the hematopoietic function and immune system. It is also toxic to the liver and kidney. There are …
-

Fluorine in the wastewater from a semiconductor plant is treated with an adsorbent after coagulating sedimentation treatment
It is believed that fluorine is an effective means of preventing cavities …
Q.What can the READ series of adsorbents adsorb?
They can adsorb inorganic anions. They do not adsorb non-ionic substances such as organic substances and complexes. The Air Water Group focus on fluorine, boron and arsenic which includes in the water quality standards.
Q.Where can it be used for water treatment?
They are used to treat a wastewater from factories, offices and tunnel excavation sites. Some products are certified as the water supply materials and equipment which can be used at restaurants to purify potable water. However, you need to pretreat the water-containing suspended solids (SS) to prevent net clogging and/or drift.
Q.At what concentration of the adsorbents can be used?
The treatment concentration differs along with the quality of raw water. Although, fluorine, boron and arsenic can be treated to a level that meets the wastewater and environmental standards specified by law. However, there is an upper limit to adsorption capacity. We recommend that any substance that exists in high concentration in the wastewater should be reduced to an appropriate level with pretreatment procedures such as coagulation sedimentation. For the specific applicable concentration depends on processing conditions, please feel free to contact us.
Q.How long can an adsorbent be used?
Basically, the service life of adsorbent for five to seven years, though it depends on the status of use.
When the adsorption capacity has been saturated (reached at the breakthrough point), a regeneration treatment restores adsorptivity and enables to use of the product repeatedly. The time to the breakthrough point may fluctuate depending on processing conditions and design, please feel free to contact us.
